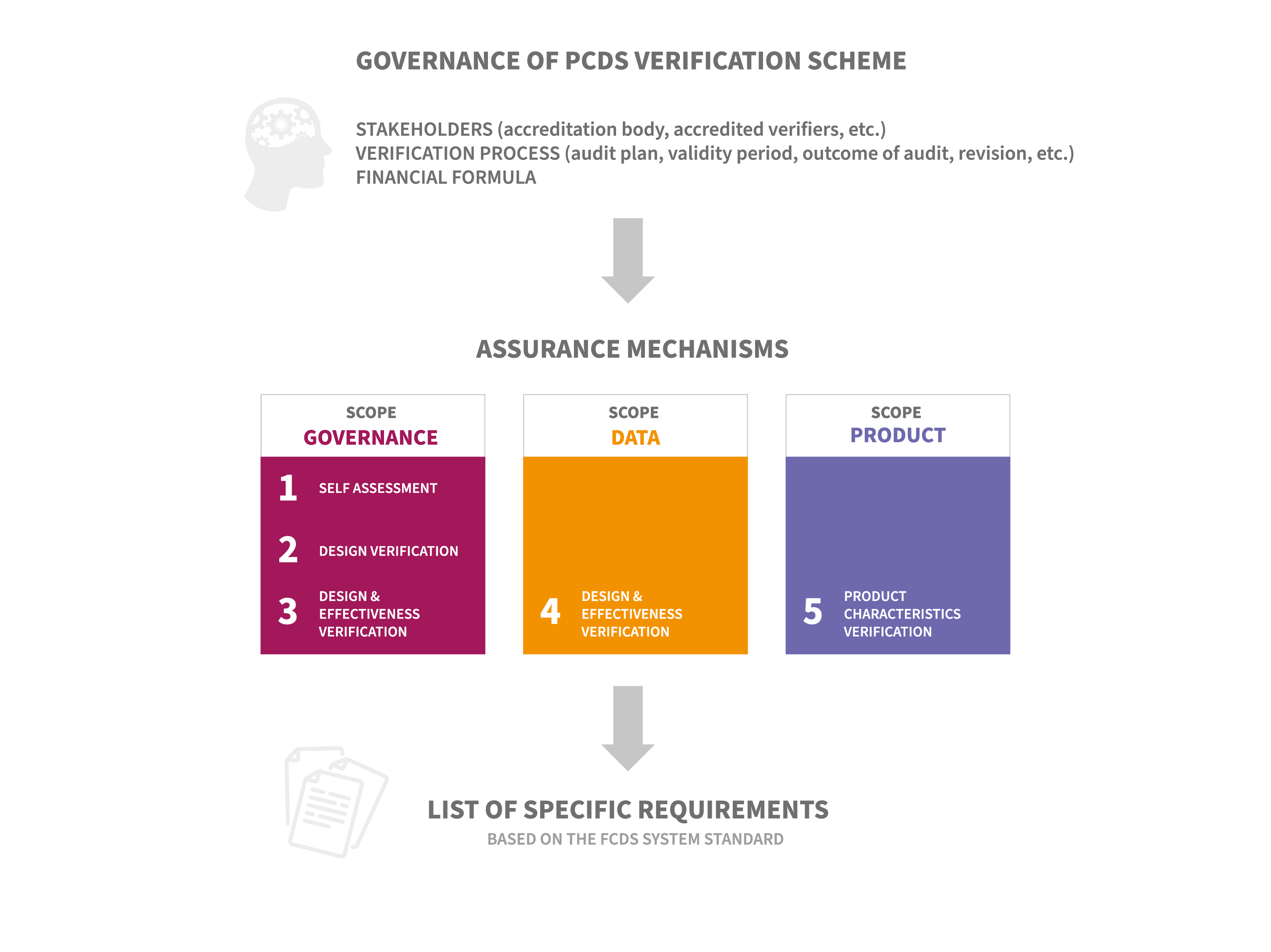
The overall idea is to provide reliable data about the circularity aspects of the product. The entry of data into the standardized PCDS template is under the full responsibility of the issuer of the document (i.e. the manufacturer of the product). Thus, a third-party verification scheme does dramatically increase the level of confidence in the provided data and is a significant added value. It also protects the manufacturer from unintentional errors in providing the market with data on e.g. product recyclability.